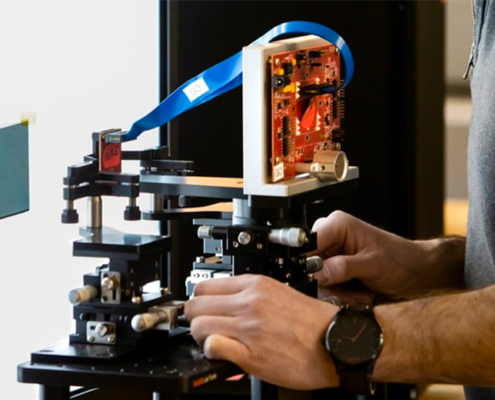
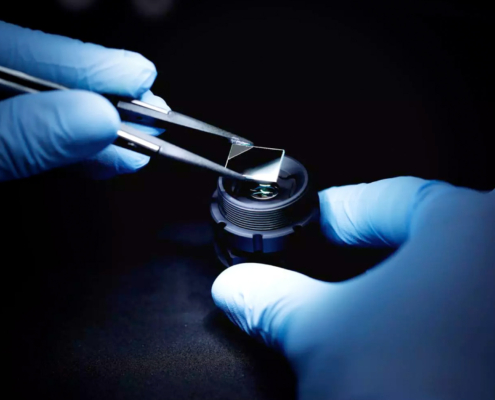
Optics plays a crucial role in the medical field across various imaging modalities. In diagnostic radiology, X-rays pass through the body and are captured on a detector or film to produce an image. Optics is critical in focusing and shaping the X-ray beam to maximize image quality while minimizing radiation exposure. Examples include:
Robotics Surgery
Robotic surgery often utilizes minimally invasive techniques, which involve making small incisions to insert surgical instruments and an imaging device. The role of optics in these procedures is to provide real-time, high-quality images from inside the patient’s body, allowing the surgeon to navigate and perform surgery with minimal physical trauma to the patient. This approach reduces recovery time, decreases the risk of infection, and minimizes scarring.
Dental Imaging
The role of optics in imaging systems for dental imagery plays a pivotal part in modern dentistry, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning, and patient outcomes. Optical imaging in dentistry encompasses various technologies, including intraoral cameras, digital X-rays, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and laser fluorescence devices, each leveraging the principles of optics to visualize the oral cavity and teeth with high precision.
Endoscopy
Endoscopy is another area where optics has been groundbreaking. This technique uses an endoscope, a flexible tube with a light and camera at the end, to explore the inside of the body. Recent optical advancements, such as capsule endoscopy, have enabled non-invasive imaging of the digestive system, vastly improving patient comfort and outcomes.